Introduction
Losing files on the Windows operating system through a delete key stroke is one of the biggest worries that a user faces. Nevertheless, there are a number of ways through which it is possible to regain these files. This guide provides a step-by-step process on how to recover deleted files and data, basic and advanced ways to do so.
Understanding File Deletion on Windows
When a file is deleted on the computer system running Windows, it is normally transferred to the Recycle Bin. This means that when the Recycle Bin is emptied the file is not lost in as much as it is still marked in the drive as free space. Using the results of the scanning of the file, different methods of its recovery can be used depending on the status of the file.
Immediate Actions to Take
- Stop Using the Drive
To increase the likelihood of recovery, avoid using the drive from which the file was deleted. Continued use may overwrite the space where the file was stored, making recovery more difficult.
- Check the Recycle Bin
The Recycle Bin is the first place to look for deleted files. If the file is found here, recovery is straightforward.
Recovering from the Recycle Bin

- Open the Recycle Bin
-
- Double-click the Recycle Bin icon on your desktop to open it.
- Locate the Deleted File
-
- Browse through the items or use the search function in the upper-right corner to find the file.
- Restore the File
-
- Right-click on the file.
- Select “Restore” from the context menu. The file will be restored to its original location.
Using File History for Recovery
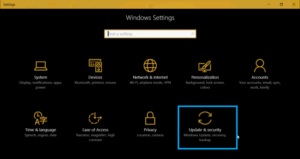
File History is Windows’ built-in backup feature. If you have been using File History, you can recover files from these backups.
- Open Control Panel
-
- Go to Control Panel > System and Security > File History.
- Browse Backups
-
- If File History is enabled, browse through the available backups to locate the file.
- Restore the File
-
- Select the file you want to recover.
- Click “Restore” to return it to its original location.
Utilizing Previous Versions
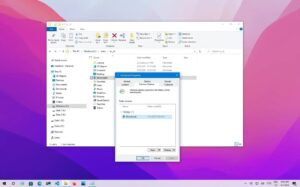
Previous Versions are another way to recover files from backups or restore points.
- Navigate to the Folder
-
- Go to the folder where the file was originally located.
- Access Folder Properties
-
- Right-click on the folder and select “Properties” from the context menu.
- Check Previous Versions
-
- Go to the “Previous Versions” tab.
- Browse through the available versions to find one that contains the deleted file.
- Restore the File
-
- Select a version from before the file was deleted.
- Click “Restore” to recover the file.
Employing Third-Party Recovery Software

If the file is not found in the Recycle Bin, File History, or Previous Versions, third-party recovery software may be needed.
- Choose Recovery Software
-
- Download a reliable recovery tool like Recuva, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, or Stellar Data Recovery from a trusted source.
- Install the Software
-
- Follow the installation instructions to set up the recovery software on your Windows PC.
- Run the Software
-
- Open the recovery application and select the drive where the file was deleted.
- Scan for Deleted Files
-
- Start a scan to search for deleted files on the selected drive. The scanning process may take some time.
- Recover the File
-
- Review the scan results to find the deleted file.
- Select the files you wish to recover and click “Recover.” Save the recovered files to a different location to avoid overwriting.
Advanced Recovery Techniques

- Command Prompt
-
- Use Command Prompt commands to attempt recovery of deleted files. This method is more complex and recommended for advanced users.
- Professional Data Recovery Services
-
- For severe data loss situations, professional data recovery services may be required. These services are equipped to handle complex recovery scenarios but may involve a cost.
Preventing Future Data Loss

- Regular Backups
-
- Use Windows Backup or third-party solutions to create regular backups of your data. Schedule automatic backups to ensure your files are consistently protected.
- Cloud Storage
-
- Utilize cloud storage services like One Drive, Google Drive, or Dropbox as an additional layer of protection. Cloud storage can serve as a secondary backup to safeguard your files.
- File Management Practices
-
- Implement good file management practices, such as organizing files into folders and naming them descriptively, to minimize the risk of accidental deletions.
Conclusion
Recovering deleted files on Windows is achievable with the right methods and tools. By following the detailed steps provided, you can effectively restore lost data and reduce the impact of accidental deletions. For advanced recovery needs or professional assistance, KnoTra Global IT Support Services is available to offer expert support and solutions to help you recover and secure your important files.

As the IT & Marketing Director at KnoTra Global, Ravi leverages over 16 years of expertise in IT, digital marketing and business consulting to enhance the client company’s strategic initiatives. His role is pivotal in integrating advanced marketing strategies with KnoTra Global’s extensive IT services, enriching our cybersecurity, cloud solutions, and IT support. Ravi’s innovative leadership ensures that KnoTra Global remains at the technological forefront, empowering our clients with robust tools and strategies for sustainable growth and success. His approach drives the company’s vision forward and sets a benchmark in delivering client-centric IT solutions.

